Dizygotic Twins
Click on the links below.
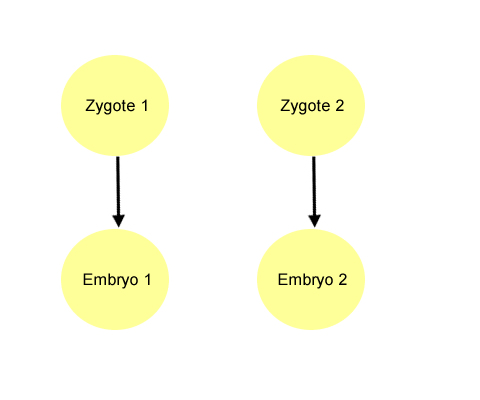
A dizygotic twin pregnancy arises from fertilisation of two eggs, each fertilised by one sperm. Each egg develops into an embryo, resulting in two fetuses.
This is the most common form of twin pregnancy. These are non-identical twins.
The two zygotes each develop into an embryo with its own chorionic sac and amniotic sac. The development of two chorionic sacs and two amniotic sacs means there are two separate placentas and there is a thick intertwin membrane. Dizygotic twins always result in dichorionic-diamniotic (DC-DA) twins.
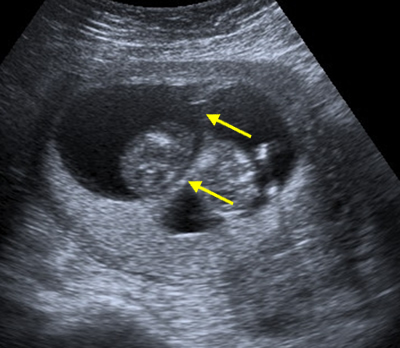
DCDA twins
A DCDA pregnancy has two chorionic sacs and two amniotic sacs which forms a thick appearance, like a wedge of tissue, where they join the placenta. This feature is called the lambda sign. The lambda sign indicates a DCDA pregnancy.
There is a thick inter-twin membrane in DCDA twins. It is more difficult to assess the lambda sign and the inter-twin membrane thickness later in pregnancy.
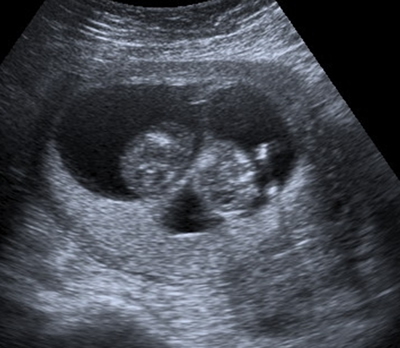
DCDA twins
A DCDA pregnancy has two chorionic sacs and two amniotic sacs which forms a thick appearance, like a wedge of tissue, where they join the placenta. This feature is called the lambda sign. The lambda sign indicates a DCDA pregnancy.
There is a thick inter-twin membrane in DCDA twins. It is more difficult to assess the lambda sign and the inter-twin membrane thickness later in pregnancy.
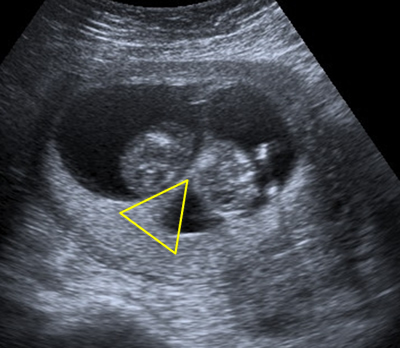
DCDA twins
A DCDA pregnancy has two chorionic sacs and two amniotic sacs which forms a thick appearance, like a wedge of tissue, where they join the placenta. This feature is called the lambda sign. The lambda sign indicates a DCDA pregnancy.
There is a thick inter-twin membrane in DCDA twins. It is more difficult to assess the lambda sign and the inter-twin membrane thickness later in pregnancy.