Echoes Issue No. 24 [DECEMBER 2020]
June 22, 2021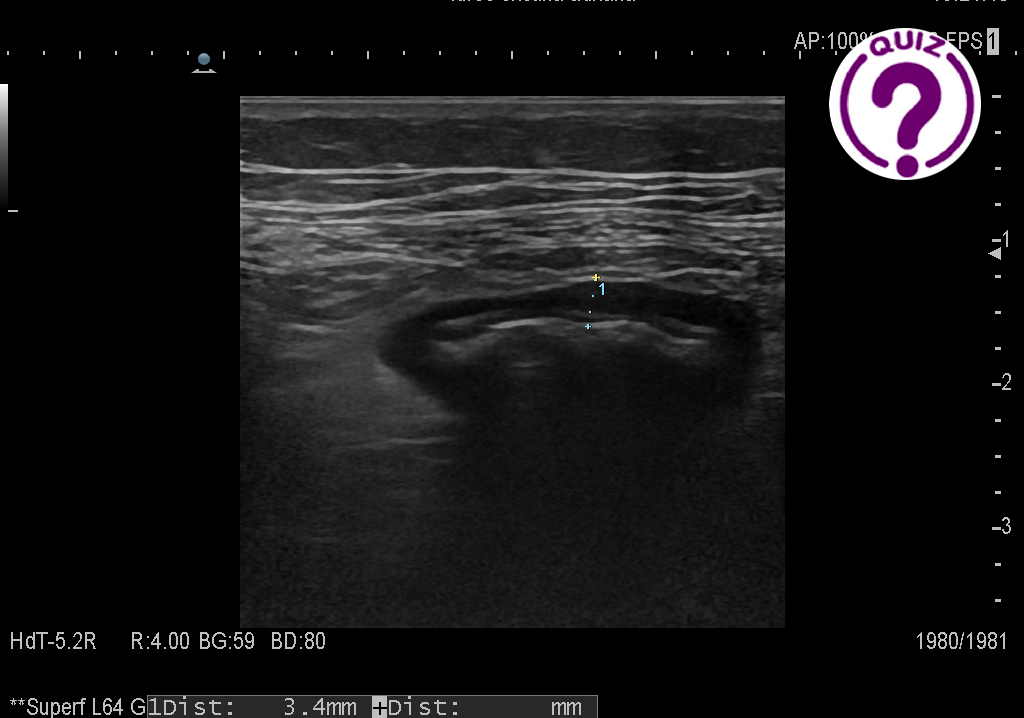
Case of the Month August 2021- Clinical picture vs imaging findings: an ultrasound surprise
August 5, 2021Jonathan Cohen 1*
1 Department of Radiology, Copenhagen University Hospital, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, Denmark; mailjonathancohen@gmail.com
* Correspondence: mailjonathancohen@gmail.com
Clinical History:
A 44-year-old male presented to our clinic with swollen inguinal lymph nodes on the left side for about 2 weeks. The lymph nodes were tender on palpation, but there was no discoloring on the skin. The patient had no fever, was in good physical shape and did not suffer from any illnesses. Two weeks previously the patient had stayed at a vacation home in a forest, and remembered one day having removed a few small ticks walking on his leg. He had had no signs of erythema migrans, wounds or swelling on the leg.
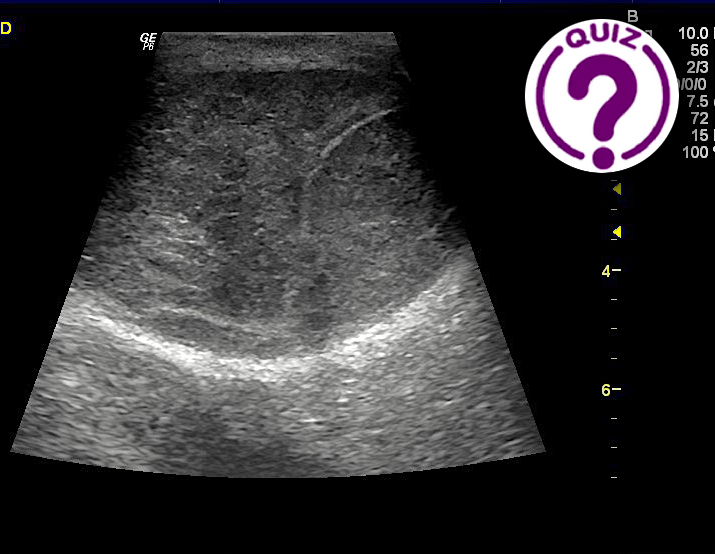
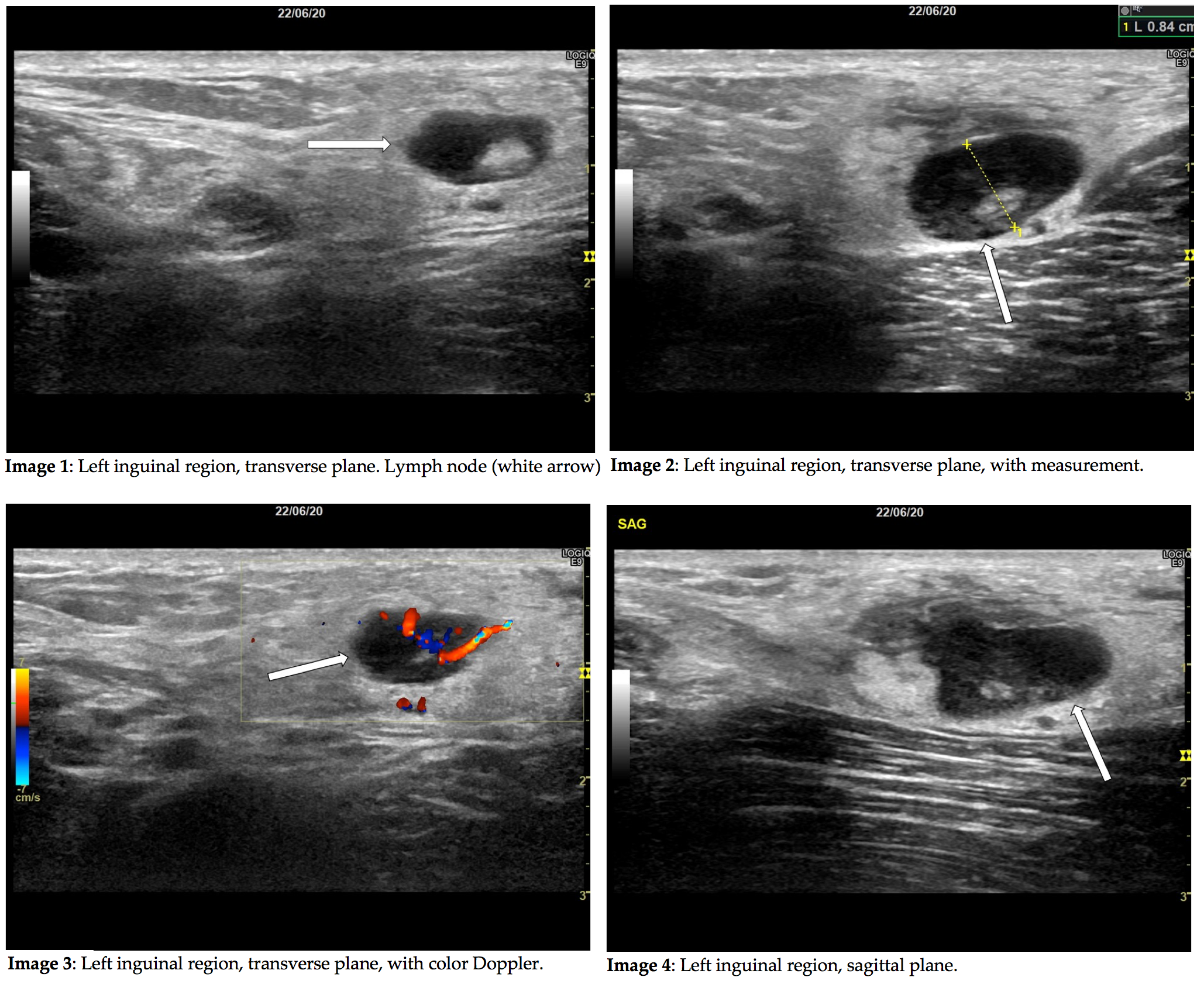
An initial ultrasound examination was performed revealing the images below.
Quiz-summary
0 of 2 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
Information
View the May Case below, answer the question and then click check >
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 2 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 2
1. Question
Correct
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q1 is: Abnormal lymph nodes either due to abscess or malignancy.
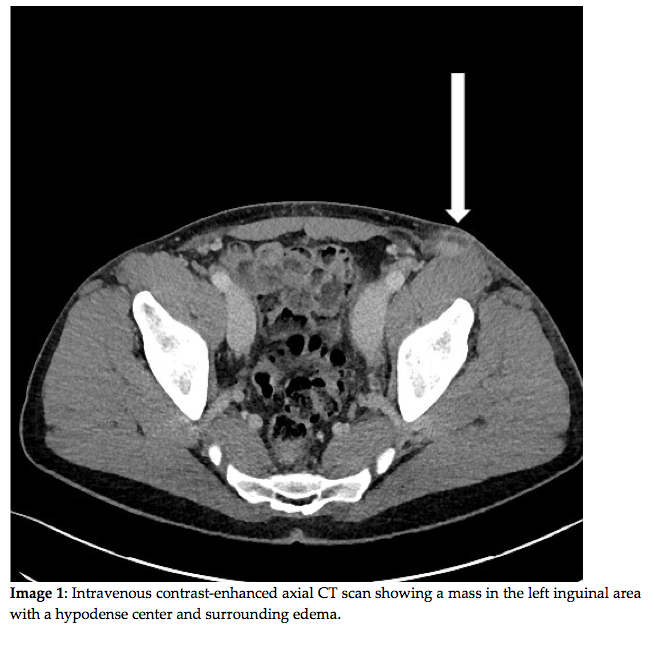
Due to the inconclusive ultrasound examination the patient was referred to a CT of the abdomen as well as further blood samples at the department of infectious diseases. The CT was inconclusive too, and a fine needle aspiration of the lymph nodes (FNA) was suggested.
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q1 is: Abnormal lymph nodes either due to abscess or malignancy.
Due to the inconclusive ultrasound examination the patient was referred to a CT of the abdomen as well as further blood samples at the department of infectious diseases. The CT was inconclusive too, and a fine needle aspiration of the lymph nodes (FNA) was suggested.
-
Question 2 of 2
2. Question
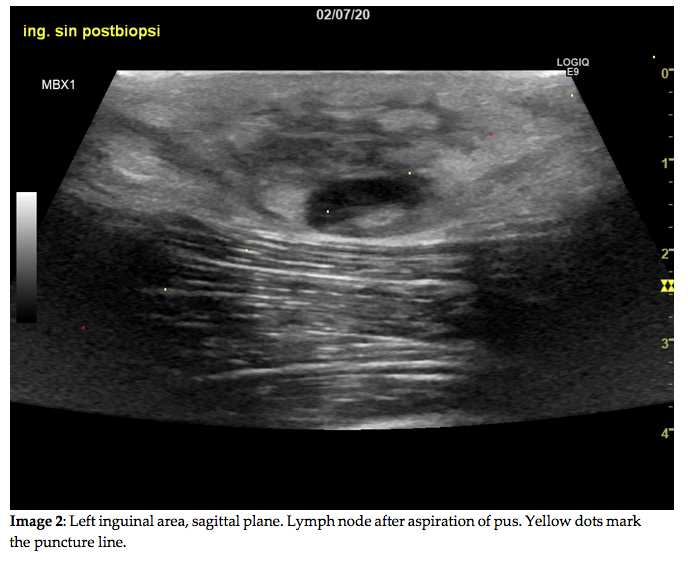
Question 2: The FNA, performed using a 0,9 mm needle, yielded only purulent exudate. A relatively rare bacterial zoonosis was found to be the cause. Which rare zoonosis is most likely the cause of the above imaging findings?
Correct
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q2 is: Tularemia.
Discussion:
Tularemia is a zoonosis caused by Francisella tularensis, a small aerobe gram-negative rod. Tularemia is very rare in northern Europe, with under 10 cases per year in Denmark. The most common disease vectors are rabbits and wild game, but ticks and mosquitoes can also carry and spread the infection. Typical symptoms include fever, muscle soreness, fatigue and lymphadenopathy. Diagnosis is usually confirmed using PCR or microbial culturing of samples. Oral antibiotics are effective, and complications are rare with adequate treatment. [1]
In the present case, ultrasound revealed an ovoid lymph node of moderate size, with no lobulation and no clear effacement of the hilum – typical traits of benign lymphadenitis [2]. However, the node had areas of considerable hypoechogenicity (see image 4), which is typically seen in areas of abscessing infection, or of necrosis in metastatic lymph nodes, especially in malignant melanoma. A lymph node with metastasis of malignant melanoma is typically hypoechoic and round, and the hilum may be effaced. The shape may also be irregular or lobulated. [3] When ultrasound reveals a lymph node exhibiting one or more of these traits, biopsy should be considered in order to rule out malignancy.
In the current case, purulent exudate was sampled from the lesion and cytology was not performed, as PCR soon confirmed infection with Francisella tularensis. The patient was treated with oral antibiotics, and the symptoms quickly subsided with no further complications.
As an interesting sidenote, because of the potential of Francisella tularensis to cause pulmonary tularemia through infection using aerosols, the Center for Disease Control considers tularemia to be a potential biological weapon threat. [4]
Conflicts of interest
“The authors declare no conflict of interest.”
References
- Tularæmi (harepest) Available online: https://www.ssi.dk/sygdomme-beredskab-og-forskning/sygdomsleksikon/t/tularaemi (accessed on Dec 13, 2020).
- Vassallo, P.; Wernecke, K.; Roos, N.; Peters, P.E. Differentiation of benign from malignant superficial lymphadenopathy: The role of high-resolution US. Radiology 1992, 183, 215–220.
- Patnana, M.; Bronstein, Y.; Szklaruk, J.; Bedi, D.G.; Hwu, W.J.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Prieto, V.G.; Ng, C.S. Multimethod imaging, staging, and spectrum of manifestations of metastatic melanoma. Clin. Radiol. 2011, 66, 224–236.
- CDC Tularemia | Emergency Preparedness & Response Available online: https://emergency.cdc.gov/agent/tularemia/ (accessed on Dec 13, 2020).
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q2 is: Tularemia.
Discussion:
Tularemia is a zoonosis caused by Francisella tularensis, a small aerobe gram-negative rod. Tularemia is very rare in northern Europe, with under 10 cases per year in Denmark. The most common disease vectors are rabbits and wild game, but ticks and mosquitoes can also carry and spread the infection. Typical symptoms include fever, muscle soreness, fatigue and lymphadenopathy. Diagnosis is usually confirmed using PCR or microbial culturing of samples. Oral antibiotics are effective, and complications are rare with adequate treatment. [1]
In the present case, ultrasound revealed an ovoid lymph node of moderate size, with no lobulation and no clear effacement of the hilum – typical traits of benign lymphadenitis [2]. However, the node had areas of considerable hypoechogenicity (see image 4), which is typically seen in areas of abscessing infection, or of necrosis in metastatic lymph nodes, especially in malignant melanoma. A lymph node with metastasis of malignant melanoma is typically hypoechoic and round, and the hilum may be effaced. The shape may also be irregular or lobulated. [3] When ultrasound reveals a lymph node exhibiting one or more of these traits, biopsy should be considered in order to rule out malignancy.
In the current case, purulent exudate was sampled from the lesion and cytology was not performed, as PCR soon confirmed infection with Francisella tularensis. The patient was treated with oral antibiotics, and the symptoms quickly subsided with no further complications.
As an interesting sidenote, because of the potential of Francisella tularensis to cause pulmonary tularemia through infection using aerosols, the Center for Disease Control considers tularemia to be a potential biological weapon threat. [4]
Conflicts of interest
“The authors declare no conflict of interest.”
References
- Tularæmi (harepest) Available online: https://www.ssi.dk/sygdomme-beredskab-og-forskning/sygdomsleksikon/t/tularaemi (accessed on Dec 13, 2020).
- Vassallo, P.; Wernecke, K.; Roos, N.; Peters, P.E. Differentiation of benign from malignant superficial lymphadenopathy: The role of high-resolution US. Radiology 1992, 183, 215–220.
- Patnana, M.; Bronstein, Y.; Szklaruk, J.; Bedi, D.G.; Hwu, W.J.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Prieto, V.G.; Ng, C.S. Multimethod imaging, staging, and spectrum of manifestations of metastatic melanoma. Clin. Radiol. 2011, 66, 224–236.
- CDC Tularemia | Emergency Preparedness & Response Available online: https://emergency.cdc.gov/agent/tularemia/ (accessed on Dec 13, 2020).