Case of the Month November 2021- Transoral ultrasound in a 27-year-old female with acute throat pain
WFUMB / EFSUMB Students Webinar Series: 7 October 2021
October 27, 2021WFUMB / EFSUMB Students Webinar Series: 4 November 2021
November 8, 2021Martin Garset-Zamani1* and Tobias Todsen1
1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, Denmark; martin.garset-zamani@regionh.dk
* Correspondence: martin.garset-zamani@regionh.dk
Clinical History:
A 27-year-old female with a sore throat was referred to the Ear-Nose-Throat emergency department by her general practitioner.
She had had a sore throat for one week, rapidly progressing over the last four days. She was unable to eat, and the pain radiated to the left ear.
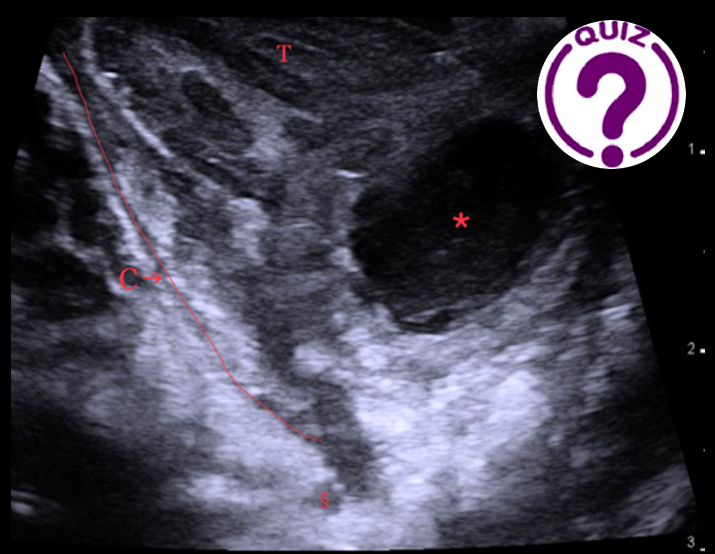
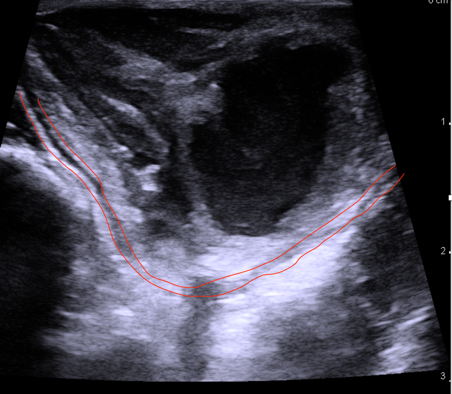
A physical examination revealed a large, firm, painful red swelling in the left tonsillar area. She had reduced opening of the jaw and the uvula deviated towards the right. A hockey-stick ultrasound probe with a frequency of 10 MHz was inserted into a rubber glove with ultrasound gel inside and introduced transorally to the left tonsil.
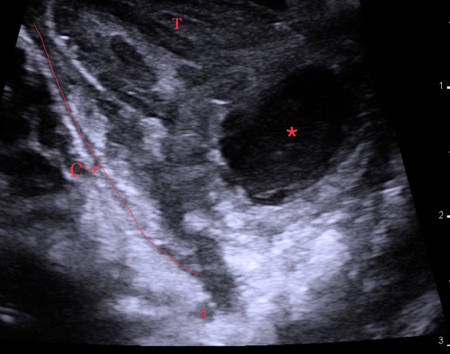
Video 1: A transoral swipe of the left tonsillar region from a cranial-to-caudal direction. The orientation is the same as in image 1.
Quiz-summary
0 of 1 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
Information
View the May Case below, answer the question and then click check >
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 1 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 1
1. Question
Question: What is the diagnosis of the lesion marked with * ?
Correct
Incorrect