Case of the Month February 2023 – Importance of diagnostic imaging in the management of a tumor lesion
Case of the Month January 2023 – 14-year-old boy with right testicular pain
January 23, 2023
Case of the Month March 2023 – Suspected finger fracture
March 2, 2023Nohelia Silva Rivas1, Rosmary Sanabria1, Abelardo Oballos1, Edda Chaves*².
1 Grupo OSEO-OSET, Caracas, Venezuela.
² Servicio de Radiología, Hospital Regional Nicolas Solano, La Chorrera, Panamá.
* Correspondence: xena.gch@gmail.com
Clinical history
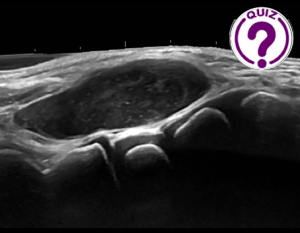
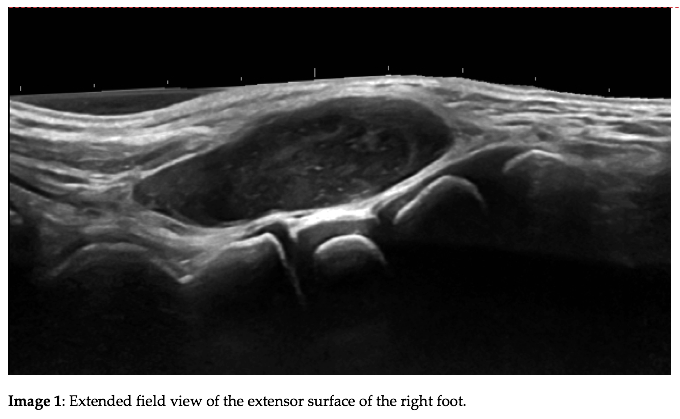
A 6-year-old patient with no previous traumatic history was referred to us for an ultrasound study (US) of a space occupying lesion located in the extensor area of the right foot (image 1). The lesion had grown rapidly, was not very painful, and did not limit the patient functionally.
Quiz-summary
0 of 4 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Information
View the May Case below, answer the question and then click check >
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 4 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 4
1. Question
Question 1: The above US findings are most compatible with:
Correct
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q1 is: Solid mass, probably malignant
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q1 is: Solid mass, probably malignant
-
Question 2 of 4
2. Question
Discussion:
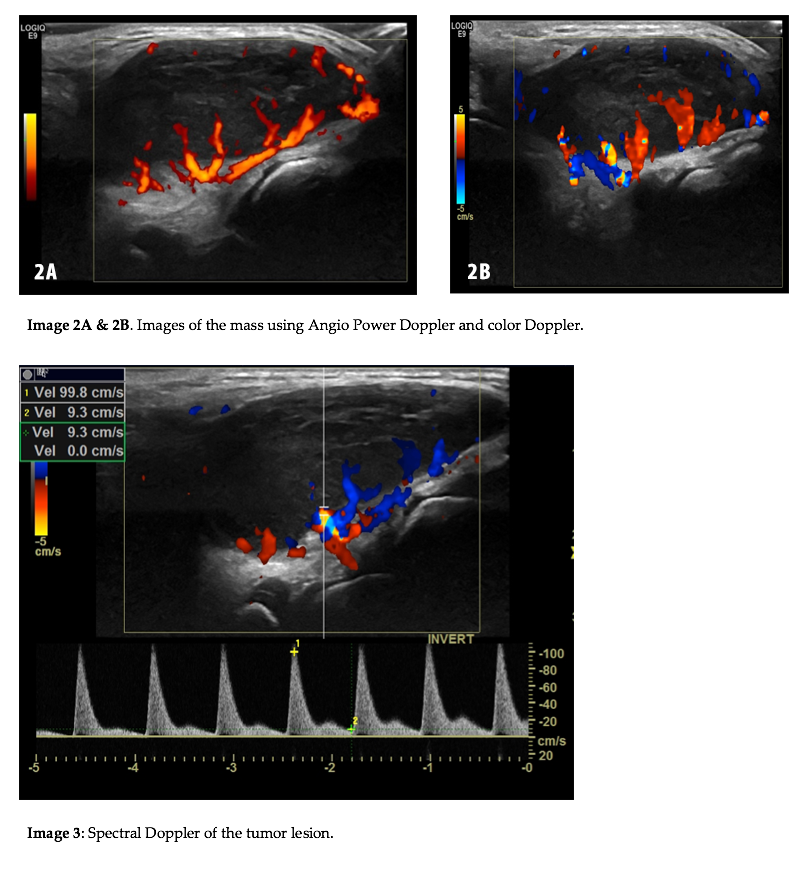
The US findings (image 1) were a very well defined, slightly heterogeneous, hypoechoic mass, located on the extensor side of the middle foot, in the muscle tendon plane. As part of the study, Doppler was performed. Color- and Angio Power Doppler revealed central and peripheral vascularization (image 2A & 2B). The spectral findings (image 3) were consistent with a monophasic high resistance arterial wave flow.
Question 2: Which additional study would you recommend?
Correct
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q2 is: MRI of the foot
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q2 is: MRI of the foot
-
Question 3 of 4
3. Question
Additional Discussion:
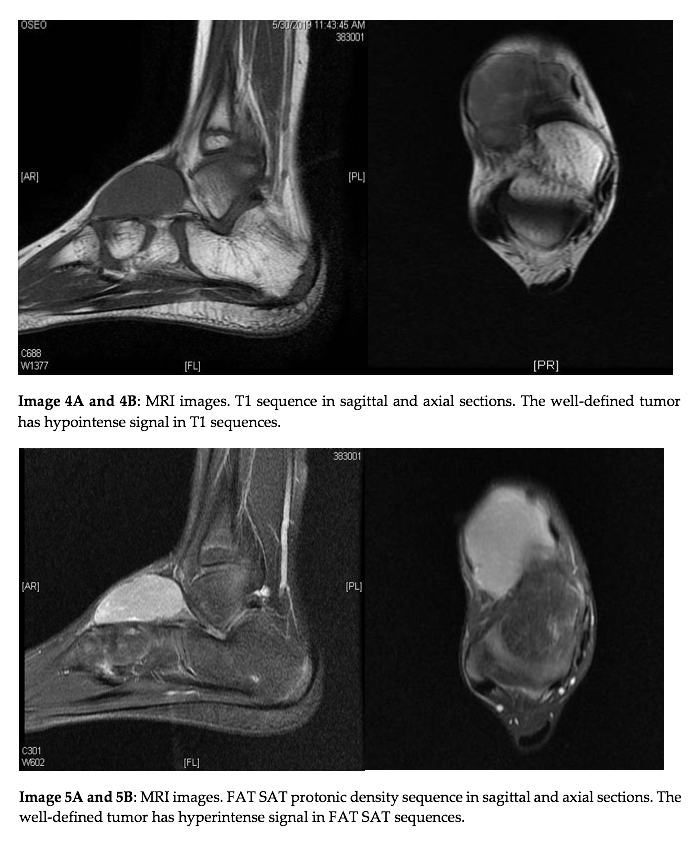
MRI was carried out as a complementary study, allowing for evaluation of, among other things, the surrounding nerves and soft tissues (image 4 & 5).
Question 3: Which of the following characteristics would you take into account to propose your diagnostic hypothesis?
Correct
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q3 is: All of the above
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q3 is: All of the above
-
Question 4 of 4
4. Question
Question 4: What are the most likely differential diagnoses to consider?
(can be more than one answer)
Correct
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q4 is: Synovial sheath tumor & Peripheral nerve tumor
Additional Discussion:
US and MRI were highly suggestive of a tumor of neurogenic origin. Resection was performed, and histopathology concluded that the tumor was a malignant mesenchymal neoplasia that corresponded to a malignant tumor of peripheral nerves.
Conclusion
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs), also called malignant Schwannoma, neurofibrosarcoma, malignant neurilemoma or neurogenic sarcoma, are malignant neoplastic lesions originating in the Schwann cells of the sheath of peripheral nerve linings [1, 2]. They may arise at any age, and have no gender predilection [6].
MPNSTs are rare, aggressive soft tissue tumors. Fifty per cent of cases occur in the context of neurofibromatosis type 1 [6]. They are most often located in the deep parts of the head, neck, spine and lower limbs [3], and are responsible for about 5% of soft tissue sarcomas [2]. MPNSTs have a risk of local regional reocurrence and distant metastases [4]. They may also differentiate into rhabdomyosarcoma, osteosarcoma or chondrosarcoma.
Conflicts of interest
“The authors declare no conflict of interest.”
References
- Weiss, S.W.: Malignant tumours of peripheral nerves. In: Enzinger FM, Weiss SW, editors. Soft tissue tumors. St. Louis: C.V. Mosby; 2008. p 903-941.
- Woodruff, J.M., Kourea, H.P., Louis, D.N., Scheithauer, BW.: Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST). In: Kleihues P, Cavenee WK, eds. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Nervous System. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2000: 172-174. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours.
- Minovi, A., Basten, O., Hunter, B., Draf, W., Bockmühl, U.: Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours of the head and neck: management of 10 cases and literature review. Head Neck. 2007; 29: 439-445.
- Anghileri, M., Miceli, R., Fiore, M., et al.: Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors: Prognostic factors and survival in a series of patients treated at a single institution. Cancer 2006; 107: 1065-1074.
- Huang, L., Espinoza, C., Welsh, R.: Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor with divergent differentiation. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003; 127: e147-50.
- Farid M, Demicco EG, Garcia R, Ahn L, Merola PR, Cioffi A, Maki RG. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Oncologist. 2014 Feb;19(2):193-201. doi: 10.1634/ the 2013-0328. Epub 2014 Jan 27. PMID: 24470531; PMCID: PMC3926794.
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q4 is: Synovial sheath tumor & Peripheral nerve tumor
Additional Discussion:
US and MRI were highly suggestive of a tumor of neurogenic origin. Resection was performed, and histopathology concluded that the tumor was a malignant mesenchymal neoplasia that corresponded to a malignant tumor of peripheral nerves.
Conclusion
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs), also called malignant Schwannoma, neurofibrosarcoma, malignant neurilemoma or neurogenic sarcoma, are malignant neoplastic lesions originating in the Schwann cells of the sheath of peripheral nerve linings [1, 2]. They may arise at any age, and have no gender predilection [6].
MPNSTs are rare, aggressive soft tissue tumors. Fifty per cent of cases occur in the context of neurofibromatosis type 1 [6]. They are most often located in the deep parts of the head, neck, spine and lower limbs [3], and are responsible for about 5% of soft tissue sarcomas [2]. MPNSTs have a risk of local regional reocurrence and distant metastases [4]. They may also differentiate into rhabdomyosarcoma, osteosarcoma or chondrosarcoma.
Conflicts of interest
“The authors declare no conflict of interest.”
References
- Weiss, S.W.: Malignant tumours of peripheral nerves. In: Enzinger FM, Weiss SW, editors. Soft tissue tumors. St. Louis: C.V. Mosby; 2008. p 903-941.
- Woodruff, J.M., Kourea, H.P., Louis, D.N., Scheithauer, BW.: Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST). In: Kleihues P, Cavenee WK, eds. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Nervous System. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2000: 172-174. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours.
- Minovi, A., Basten, O., Hunter, B., Draf, W., Bockmühl, U.: Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours of the head and neck: management of 10 cases and literature review. Head Neck. 2007; 29: 439-445.
- Anghileri, M., Miceli, R., Fiore, M., et al.: Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors: Prognostic factors and survival in a series of patients treated at a single institution. Cancer 2006; 107: 1065-1074.
- Huang, L., Espinoza, C., Welsh, R.: Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor with divergent differentiation. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003; 127: e147-50.
- Farid M, Demicco EG, Garcia R, Ahn L, Merola PR, Cioffi A, Maki RG. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Oncologist. 2014 Feb;19(2):193-201. doi: 10.1634/ the 2013-0328. Epub 2014 Jan 27. PMID: 24470531; PMCID: PMC3926794.