Webinar: Gastrointestinal ultrasound (GIUS) in IBD – 11-03-2024
January 4, 2024
Webinar: WFUMB European CoE – 22-02-2024
January 16, 2024Camilla Palmquist Frykman1* and Chenxi Huang2
1 Department of Radiology, Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, Denmark; camilla.palmquist.frykman.@regionh.dk
2 Department of Radiology, Copenhagen University Hospital Rigshospitalet; chenxi.huang.01@regionh.dk
* Correspondence: camilla.palmquist.frykman@regionh.dk
Clinical history
A 62-year-old man with a history of metastatic colorectal cancer had previously been treated with chemotherapy and by a combination of extensive radiofrequency ablation and resection of liver segments. A 3-month follow-up CT scan of the liver revealed possible relapse of liver metastases, but also possible abscesses. CRP was 80 mg/L. The CT was supplemented with an MRI with and without liver specific contrast agent and diffusion sequences. The MRI showed multiple lesions, among them a collection of fluid with diffusion restriction in one of the resection cavities which could be an abscess, but also other lesions that resembled metastases. Due to the large size and rapid growth of one of the lesions it was unclear whether it was a metastasis or an abscess. To clarify the diagnosis of this lesion the patient was referred to an ultrasound (US) examination with intravenous contrast agent and a supplemental biopsy for pathological and microbiological examination.
Images
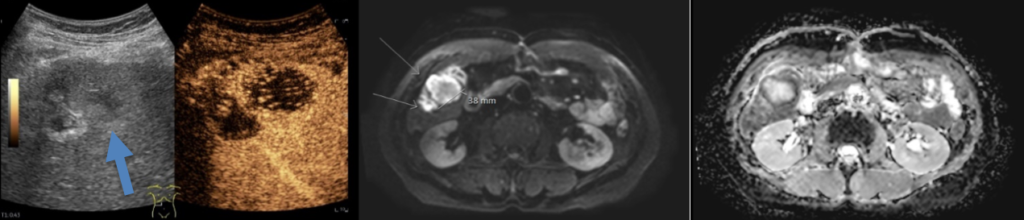
Image 1: US of the liver in the right lateral intercostal space, axial plane. A. CEUS examination, arterial phase. The lesion has rapid wash-in and rapid wash-out of intravenous contrast agent. B. Same lesion on MRI, diffusion weighted sequence b800 and C. corresponding ADC map.
Quiz-summary
0 of 3 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
Information
View the January Case below, answer the question and then click check >
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 3 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 3
1. Question
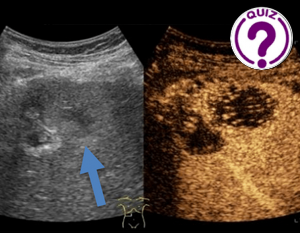
Question 1: What is the most likely diagnosis of the lesion marked by arrows?
Correct
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q1 is: Metastasis
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q1 is: Metastasis
-
Question 2 of 3
2. Question
Discussion:
The metastasis in image 1 (after administration of US contrast agent) showed classic malignant enhancement features (rapid wash-in and rapid wash out due to the arterial blood supply). On conventional b-mode US images, metastases can appear as hypo-, hyper or isoechoic lesions (1-2), most often hypoechoic (65%) (2).
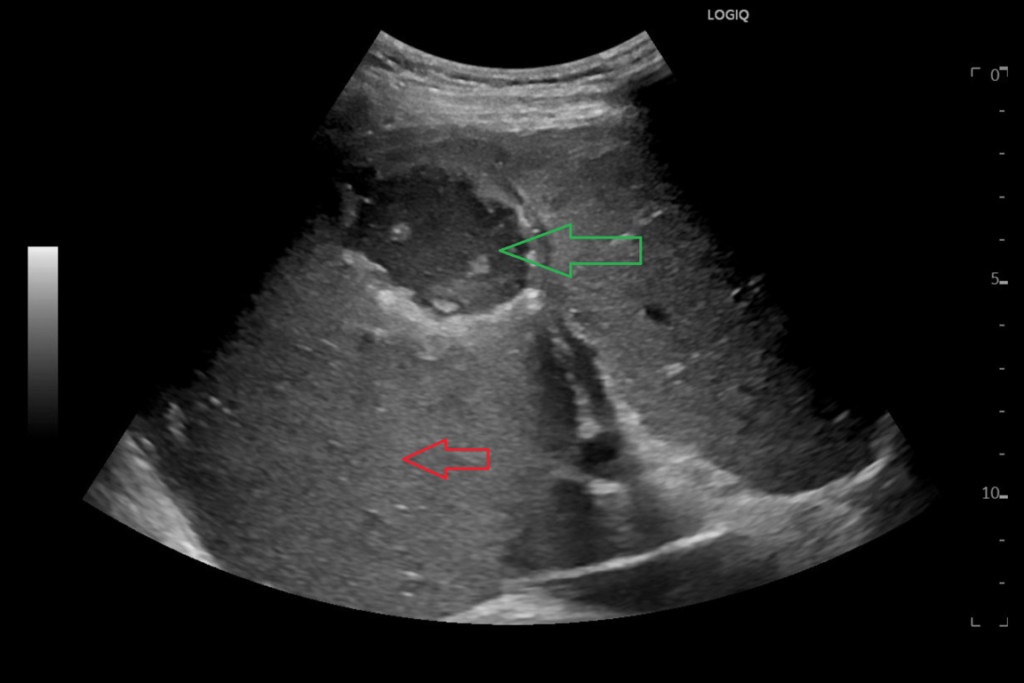
As the central part of the metastasis did not enhance and the lesion was quite large (rapid growth) it was decided to do a biopsy, which could also guide future oncological treatment. Pathological examination revealed tumor cells of mucinous adenocarcinoma. A different intrahepatic finding had the following appearance on B-mode US:Image 2: US of the liver in the right lateral intercostal space, semicoronal plane. Another lesion in the liver had this appearance and did not enhance after contrast agent.
Question 2: What does a) the red arrow and b) the green arrow mark, respectively?
Correct
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q2 is: a) normal liver tissue, and b) liver lesion
Additional discussionThe red arrow marks normal homogenous and normoechoic liver tissue, whilst the green arrow marks the liver lesion with a hypoechoic content and areas of debris. The green arrow does not resemble a gallbladder with cholecystolithiasis, since gall bladder stones tend to collect at the dependent point of the gallbladder. CEUS confirmed that the lesion was an abscess.
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q2 is: a) normal liver tissue, and b) liver lesion
Additional discussionThe red arrow marks normal homogenous and normoechoic liver tissue, whilst the green arrow marks the liver lesion with a hypoechoic content and areas of debris. The green arrow does not resemble a gallbladder with cholecystolithiasis, since gall bladder stones tend to collect at the dependent point of the gallbladder. CEUS confirmed that the lesion was an abscess.
-
Question 3 of 3
3. Question
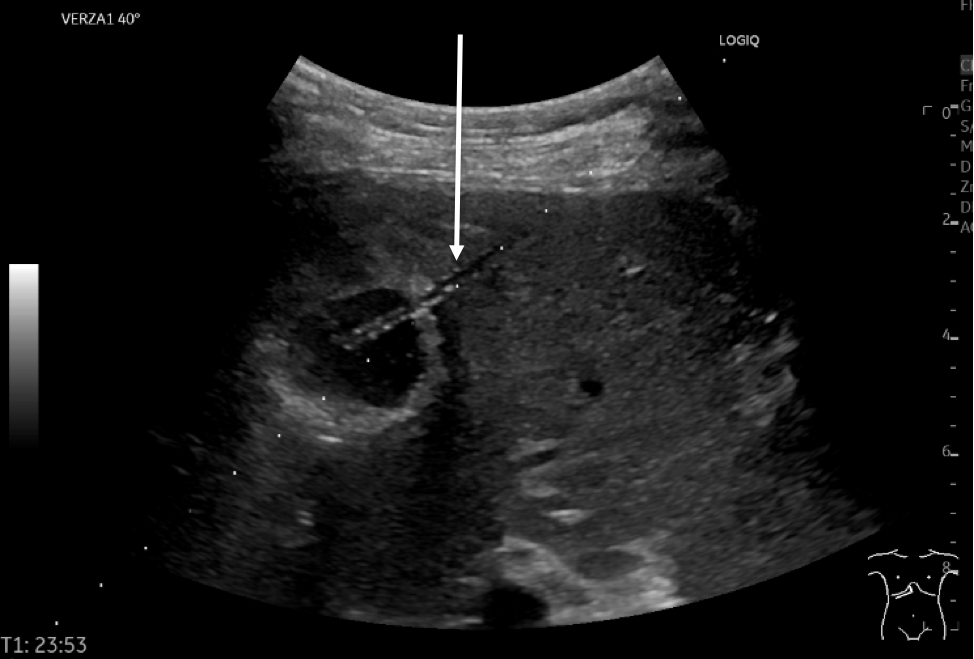
Image 3: US of the liver in the right lateral intercostal plane, semicoronal plane. Same lesion as in Image 2.
Question 3: What does the white arrow mark?
Correct
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q3 is: Catheter in the liver abscess
Additional Discussion:
The dots on the image are aligned with a distance of 1 cm functioning as guidance for depth of the catheter or a biopsy needle. The hyperechoic catheter is inserted along the dots with its tip approximately in the center of the liver lesion after retraction of the stylet.
Conclusion
Liver metastases can present as hypo-, hyper- or isoechoic lesions (if visible on ultrasound). When supplementing with ultrasound contrast agent, liver metastases usually show rapid contrast enhancement and rapid wash-out compared to the surrounding normal liver tissue due to their arterial blood supply. In this case the mucinous adenocarcinoma metastasis resembled an abscess on US (and on CT and MRI) before administration of intravenous US contrast agent due to its necrotic center.
It is important to be aware of malignancy as a differential diagnosis in seemingly benign lesions such as abscesses, especially in cancer patients and vice versa. US is a useful tool to help with differentials and guide biopsy.
Conflicts of interest
“The authors declare no conflict of interest.”
References
- Lincke T; Zech CJ. Liver metastases: Detection and staging. Eur J Radiol, 2017, 97, 76-82.
- Freitas PS; Janicas C; Veiga J; Matos AP; Herédia V; Ramalho M. Imaging evaluation of the liver in oncology patients: A comparison of techniques. World J Hepatol. 2021, 13(12), 1936-1955.
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q3 is: Catheter in the liver abscess
Additional Discussion:
The dots on the image are aligned with a distance of 1 cm functioning as guidance for depth of the catheter or a biopsy needle. The hyperechoic catheter is inserted along the dots with its tip approximately in the center of the liver lesion after retraction of the stylet.
Conclusion
Liver metastases can present as hypo-, hyper- or isoechoic lesions (if visible on ultrasound). When supplementing with ultrasound contrast agent, liver metastases usually show rapid contrast enhancement and rapid wash-out compared to the surrounding normal liver tissue due to their arterial blood supply. In this case the mucinous adenocarcinoma metastasis resembled an abscess on US (and on CT and MRI) before administration of intravenous US contrast agent due to its necrotic center.
It is important to be aware of malignancy as a differential diagnosis in seemingly benign lesions such as abscesses, especially in cancer patients and vice versa. US is a useful tool to help with differentials and guide biopsy.
Conflicts of interest
“The authors declare no conflict of interest.”
References
- Lincke T; Zech CJ. Liver metastases: Detection and staging. Eur J Radiol, 2017, 97, 76-82.
- Freitas PS; Janicas C; Veiga J; Matos AP; Herédia V; Ramalho M. Imaging evaluation of the liver in oncology patients: A comparison of techniques. World J Hepatol. 2021, 13(12), 1936-1955.