Using ACR BI-RADS Lexicon Ultrasound Descriptors in Clinical Practice ~ Sudhir Vinayak (Kenya)
October 24, 2022
Ultrasound features of different breast cancers ~ Boris Brkljacic (Croatia)
November 2, 2022Douira-Khomsi Wièm
Department of Paediatric radiology, Béchir Hamza Children’s Hospital, Tunis, Tunisia
* Correspondence: Khomsiwiem@yahoo.fr
Clinical history
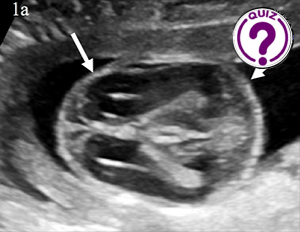
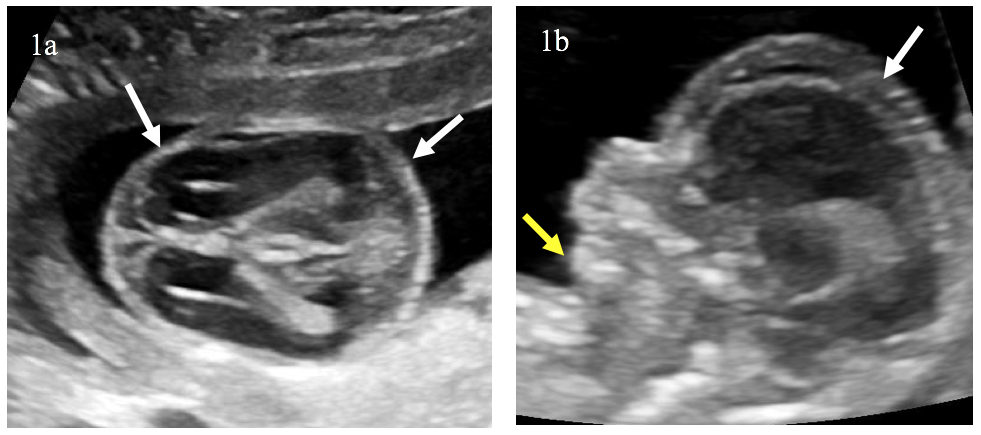
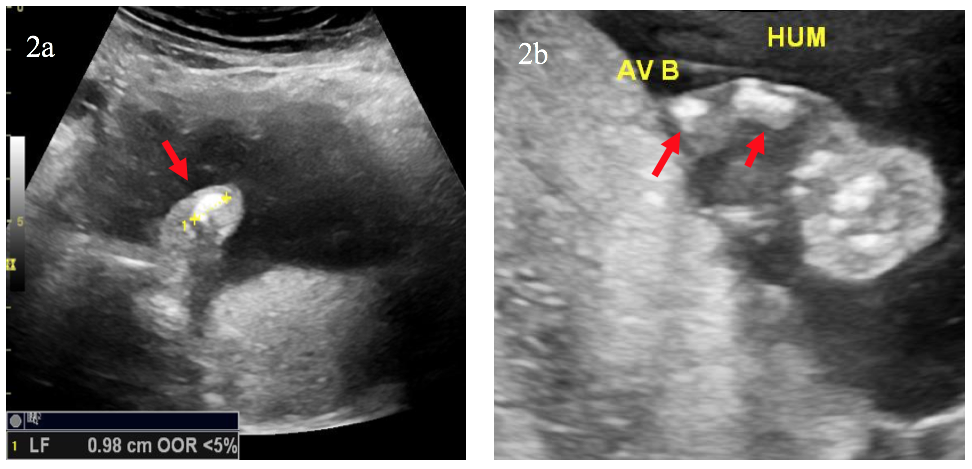
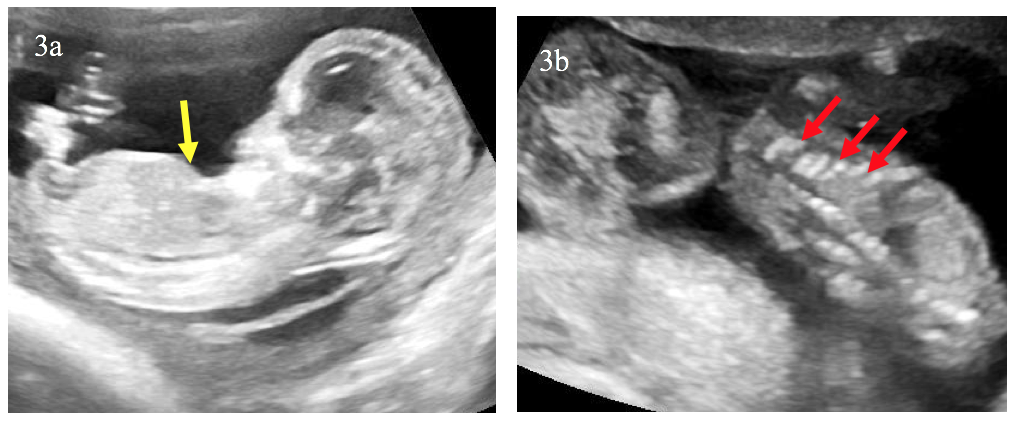
A 30-year-old pregnant woman was referred to our department at 16 weeks’ gestation, a routine antenatal ultrasound identified multiple skeletal abnormalities.
Images / Videos
Quiz-summary
0 of 1 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
Information
View the May Case below, answer the question and then click check >
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 1 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 1
1. Question
Question: Which diagnosis do you consider?
Correct
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct Answer is: Osteogenesis imperfecta
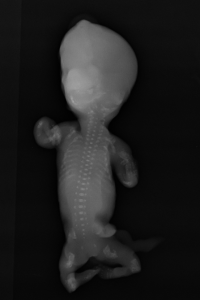
The triad of bone shortening, decreased bone density and numerous fractures including beaded ribs is consistent with the diagnosis of osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) type II. These findings were confirmed after the medical pregnancy termination by post mortem examination including fetoplacental examination, radiographs (Image 5) and biochemical studies of cultivated fibroblasts from the fetus.
Discussion
OI is a rare inherited bone disease caused by defects in type I collagen synthesis. The most widely used classification for OI distinguishes four types, based on clinical findings and disease severity, type II is the most severe form with perinatal death. It can be diagnosed by ultrasound from 14 weeks of gestation, on specific signs suchas intra-uterine growth retardation or hydramnios. Otherwise, US may show abnormalities of skull, ribs, spine or limbs: decreased echogenicity due to insufficient mineralization, deformities related to fractures, callus formation, increased bone plasticity and micromelia, especially of the femur. however, it is important to recognize that it can be difficult some times to US to distinguish between severe OI and other lethal skeletal dysplasias such as camptomelic dysplasia or thanatotropic dysplasia.
Conclusion
OI type II is a rare lethal pathology of the skeleton with severe abnormalities that may be identified by first trimester ultrasound.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no potential conflict of interest.
References
- Buisson O , Senat MV, Laurenceau N, Ville Update on prenatal diagnosis of osteogenesis imperfecta type II : an index case report diagnosed by ultrasonography in the first trimester . Case Reports. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2002 Nov; 31(7): 672-6.
- Rauch F, Glorieux FH (2004) Osteogenesis imperfecta Lancet Lond Engl 2004 Apr 24;363 (9418): 1377-85
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct Answer is: Osteogenesis imperfecta
The triad of bone shortening, decreased bone density and numerous fractures including beaded ribs is consistent with the diagnosis of osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) type II. These findings were confirmed after the medical pregnancy termination by post mortem examination including fetoplacental examination, radiographs (Image 5) and biochemical studies of cultivated fibroblasts from the fetus.
Discussion
OI is a rare inherited bone disease caused by defects in type I collagen synthesis. The most widely used classification for OI distinguishes four types, based on clinical findings and disease severity, type II is the most severe form with perinatal death. It can be diagnosed by ultrasound from 14 weeks of gestation, on specific signs suchas intra-uterine growth retardation or hydramnios. Otherwise, US may show abnormalities of skull, ribs, spine or limbs: decreased echogenicity due to insufficient mineralization, deformities related to fractures, callus formation, increased bone plasticity and micromelia, especially of the femur. however, it is important to recognize that it can be difficult some times to US to distinguish between severe OI and other lethal skeletal dysplasias such as camptomelic dysplasia or thanatotropic dysplasia.
Conclusion
OI type II is a rare lethal pathology of the skeleton with severe abnormalities that may be identified by first trimester ultrasound.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no potential conflict of interest.
References
- Buisson O , Senat MV, Laurenceau N, Ville Update on prenatal diagnosis of osteogenesis imperfecta type II : an index case report diagnosed by ultrasonography in the first trimester . Case Reports. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2002 Nov; 31(7): 672-6.
- Rauch F, Glorieux FH (2004) Osteogenesis imperfecta Lancet Lond Engl 2004 Apr 24;363 (9418): 1377-85