Is there a place for elastography for nerves evaluation? ~ Fabrizio Calliada (Italy)
January 23, 2023
Case of the Month February 2023 – Importance of diagnostic imaging in the management of a tumor lesion
February 14, 2023Solumsmoen, Stian 1, Kinder-Klausen, Maren Sofie1
1 Dept. Of Radiology, Copenhagen University Hospital, Rigshospitalet, Denmark
* Correspondence: stian.kinder.solumsmoen@regionh.dk
Clinical history
A 14-year-old boy was referred to the emergency dept. at Copenhagen University Hospital with pain in his right testicle. He had a bicycle accident two days prior where the handlebars on his bicycle hit him in his lower abdomen and groin whilst falling. He sought medical attention due to progressively increasing pain in his right testicle.
Quiz-summary
0 of 2 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
Information
View the May Case below, answer the question and then click check >
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 2 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 2
1. Question
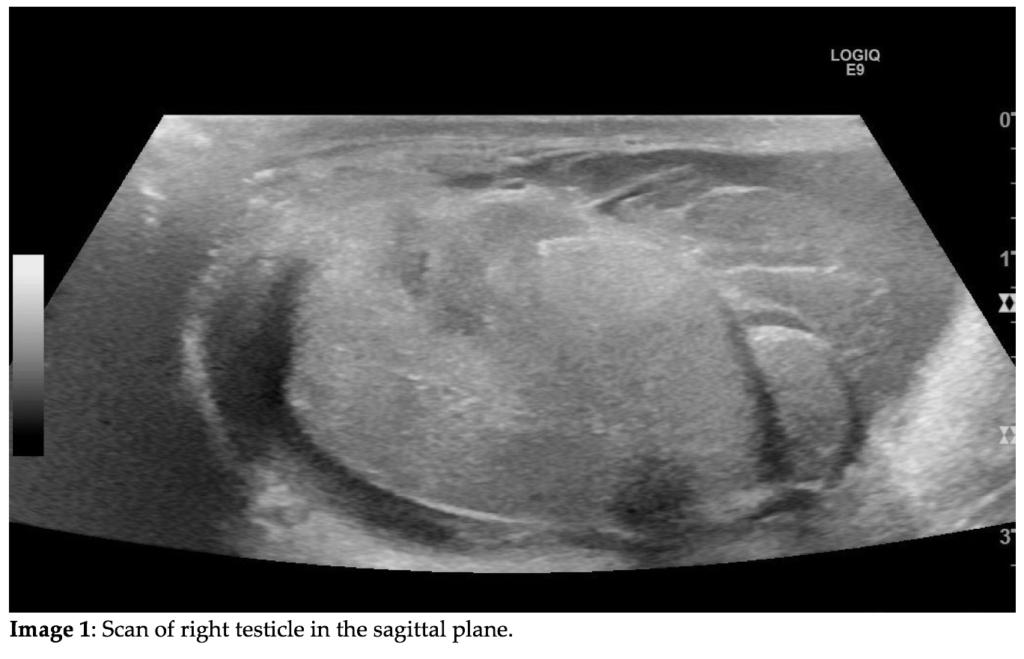
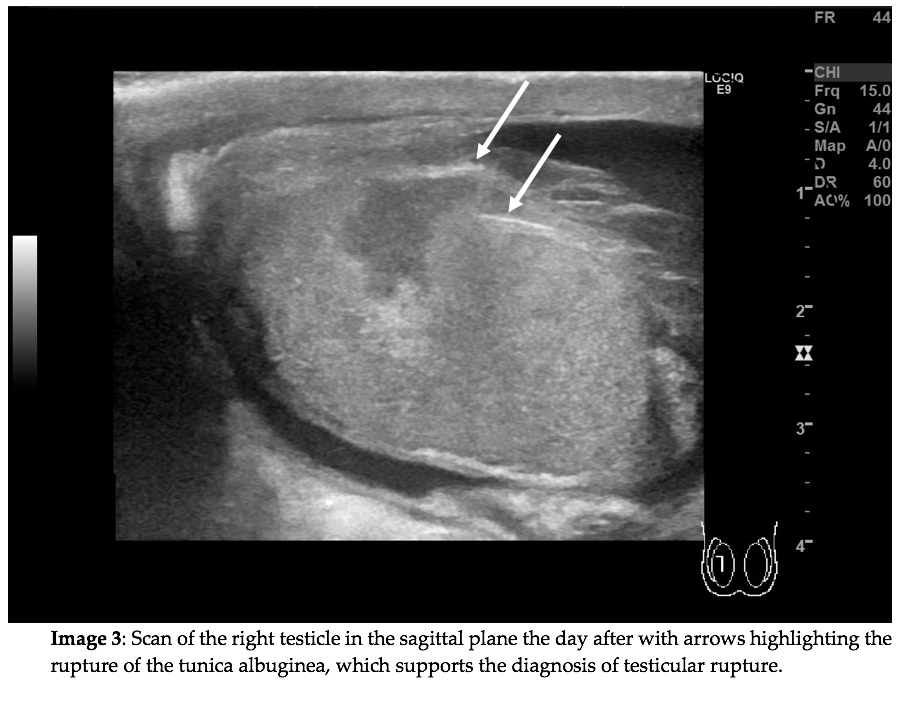
Question 1: What are the ultrasound findings on image 1?
Correct
CORRECT ANSWER
Correct answer to Q1 is: Testicular rupture
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER
Correct answer to Q1 is: Testicular rupture
-
Question 2 of 2
2. Question
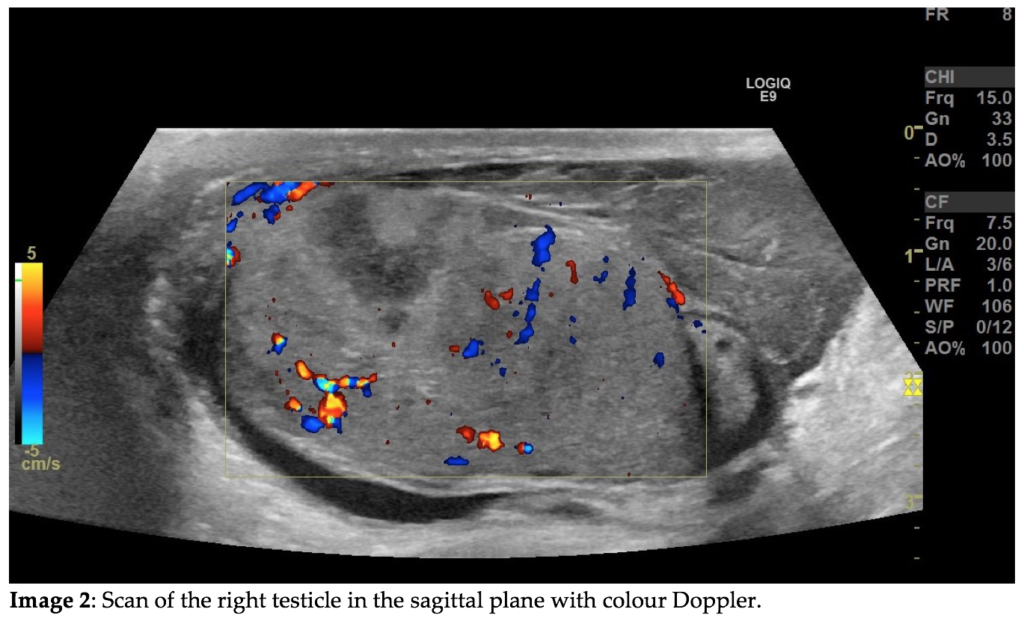
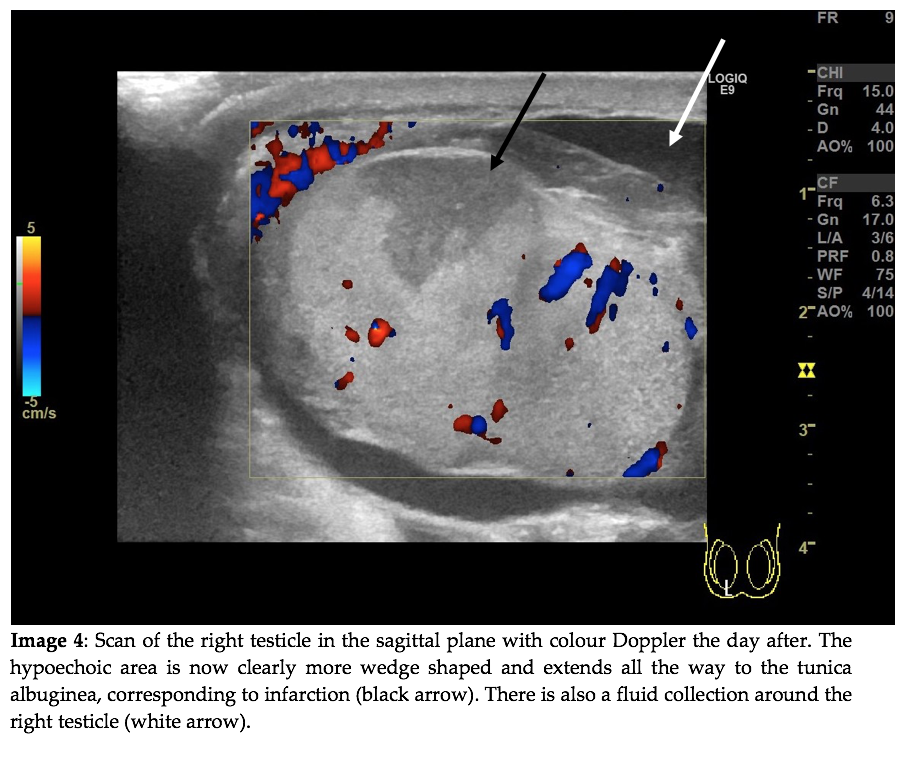
Question 2: How does image 2 confirm your initial suspicion?
Correct
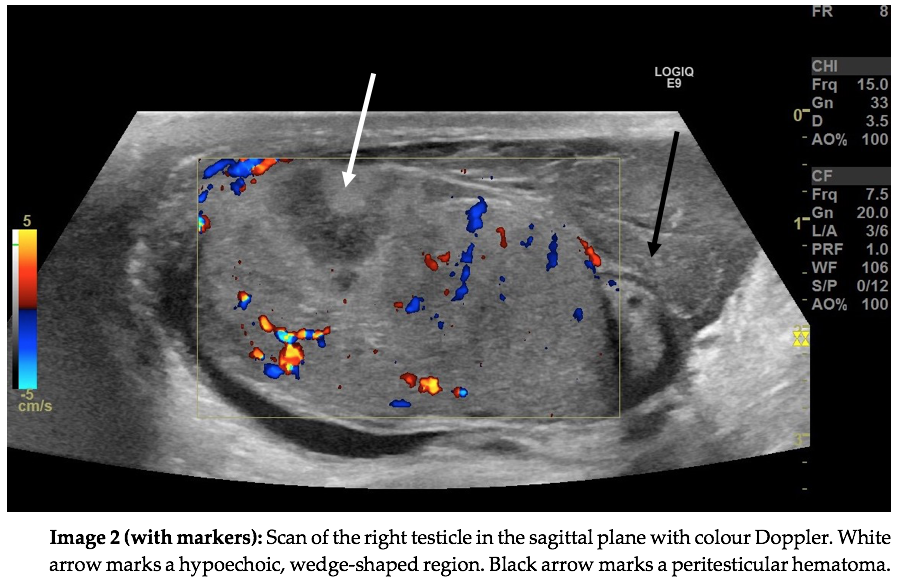
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q2 is: It shows a hypoechoic region in proximity to a discontinuity of the tunica albuginea which supports testicular rupture.
Discussion
Discontinuity of the tunica albuginea as a result of testicular rupture is an acute condition which requires surgery within 72 hours.1,2 The rupture of the testis can lead to a release of spermatic antigens with subsequent production of antisperm antibodies by the immune system. This in turn can lead to infertility.3
Testicular trauma with subsequent testicular rupture is relatively rare.1 The disruption of the tunica albuginea was not recognised on the initial scan. Instead, the hypoechogenic area without Doppler flow within the testicle was interpreted as an intratesticular hematoma. The extratesticular mass was rightfully interpreted as an extratesticular hematoma. The hematoma is highlighted by the black arrow on Image 2. On a follow-up scan the next day the testicular rupture was recognised. The hypoechogenic region had undergone further demarcation and was by then more consistent with an infarction.
Within 24 hours the 14-year-old boy underwent surgery where the right testicle was removed due to pronounced tissue necrosis.
Conclusion
Testicular rupture is an acute condition which requires surgery. When encountering an intratesticular hypoechogenic region without flow after relevant trauma the tunica albuginea should be thoroughly evaluated for any discontinuity. The findings on ultrasound may result in urgent surgery.
Conflicts of Interest:
No conflict of interest.
References
- Addas F, Yan S, Hadjipavlou M, Gonsalves M, Sabbagh S. Testicular Rupture or Testicular Fracture? A Case Report and Literature Review. Case Rep Urol. 2018;2018:1-3. doi:10.1155/2018/1323780
- Fahlbusch B, Fahlbusch M, Thon WF. Blunt testicular injury – conservative or surgical treatment? Aktuelle Urol. 2003;34(3):176-178. doi:10.1055/s-2003-40234
- Aghamir SMK, Salavati A, Yousefie R, et al. Does Bone Marrow–derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transfusion Prevent Antisperm Antibody Production After Traumatic Testis Rupture? Urology. 2014;84(1):82-86. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2014.03.009
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer to Q2 is: It shows a hypoechoic region in proximity to a discontinuity of the tunica albuginea which supports testicular rupture.
Discussion
Discontinuity of the tunica albuginea as a result of testicular rupture is an acute condition which requires surgery within 72 hours.1,2 The rupture of the testis can lead to a release of spermatic antigens with subsequent production of antisperm antibodies by the immune system. This in turn can lead to infertility.3
Testicular trauma with subsequent testicular rupture is relatively rare.1 The disruption of the tunica albuginea was not recognised on the initial scan. Instead, the hypoechogenic area without Doppler flow within the testicle was interpreted as an intratesticular hematoma. The extratesticular mass was rightfully interpreted as an extratesticular hematoma. The hematoma is highlighted by the black arrow on Image 2. On a follow-up scan the next day the testicular rupture was recognised. The hypoechogenic region had undergone further demarcation and was by then more consistent with an infarction.
Within 24 hours the 14-year-old boy underwent surgery where the right testicle was removed due to pronounced tissue necrosis.
Conclusion
Testicular rupture is an acute condition which requires surgery. When encountering an intratesticular hypoechogenic region without flow after relevant trauma the tunica albuginea should be thoroughly evaluated for any discontinuity. The findings on ultrasound may result in urgent surgery.
Conflicts of Interest:
No conflict of interest.
References
- Addas F, Yan S, Hadjipavlou M, Gonsalves M, Sabbagh S. Testicular Rupture or Testicular Fracture? A Case Report and Literature Review. Case Rep Urol. 2018;2018:1-3. doi:10.1155/2018/1323780
- Fahlbusch B, Fahlbusch M, Thon WF. Blunt testicular injury – conservative or surgical treatment? Aktuelle Urol. 2003;34(3):176-178. doi:10.1055/s-2003-40234
- Aghamir SMK, Salavati A, Yousefie R, et al. Does Bone Marrow–derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transfusion Prevent Antisperm Antibody Production After Traumatic Testis Rupture? Urology. 2014;84(1):82-86. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2014.03.009