Case of the Month March 2024 (2) – An uncommon focal liver lesion
March 15, 2024
WFUMB AFSUMB Student Webinar on Gynaecological Ultrasound
April 19, 2024Jihene Belhadj Ali, Wiém Douira-Khomsi
Department of Paediatric Radiology, Béchir Hamza Children’s Hospital, Tunis, Tunisia *
* Correspondences: bhjjihene@gmail.com ; khomsiwiem@yahoo.fr
Clinical history
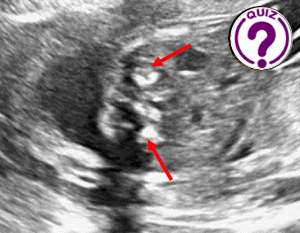
A 34-year-old pregnant woman, gravida 2 para 1, was referred to our department at 22 weeks’ gestation for routine antenatal ultrasound examination. She previously had one uncomplicated pregnancy. Her personal and family medical history were unremarkable.
Images
Quiz-summary
0 of 1 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
Information
View the April Case below, answer the question and then click check >
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 1 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 1
1. Question
Question: Which diagnosis do you consider?
Correct
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer is: Wolman disease
Discussion
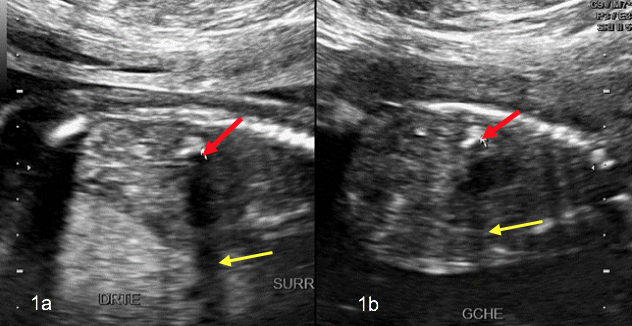
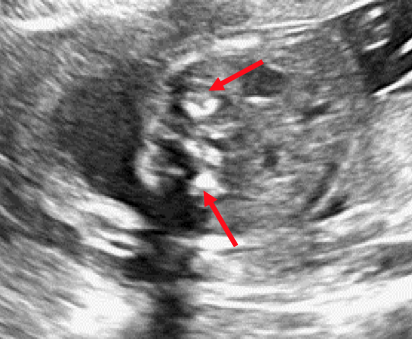
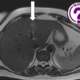
Wolman disease (WD), is a rare autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder. It results from a profound deficiency in the lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) enzyme. Tragically, it leads to fatality within the initial year of life (1). Radiological findings in WD include a characteristic pattern of stippled calcification in enlarged but normally shaped adrenal glands (1). Hepatosplenomegaly and lymphadenopathy may also be observed (2). The calcifications delineate the cortical outline only of both glands, and this sign appears to be pathognomonic for the disease. This phenomenon arises from the saponification of fatty acids followed by their calcification.
Conclusion
WD is a rare autosomal recessive lysosomal disorder that often proves fatal within the first year. A key diagnostic indicator is the presence of normally shaped, bilaterally enlarged adrenal glands with dense cortical calcifications, detectable via prenatal ultrasound, improving management.
Conflicts of Interest:
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sen D, Satija L, Saxena S, Rastogi V, Singh M. A rare constellation of imaging findings in Wolman disease. Med J Armed Forces India. dec 2015;71(Suppl 2):S448‑51.
- Sadhukhan M, Saha A, Vara R, Bhaduri B. Infant case of lysosomal acid lipase deficiency: Wolman’s disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2014 May 15;2014: bcr2013202652.
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER EXPLAINED BELOW Correct answer is: Wolman disease
Discussion
Wolman disease (WD), is a rare autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder. It results from a profound deficiency in the lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) enzyme. Tragically, it leads to fatality within the initial year of life (1). Radiological findings in WD include a characteristic pattern of stippled calcification in enlarged but normally shaped adrenal glands (1). Hepatosplenomegaly and lymphadenopathy may also be observed (2). The calcifications delineate the cortical outline only of both glands, and this sign appears to be pathognomonic for the disease. This phenomenon arises from the saponification of fatty acids followed by their calcification.
Conclusion
WD is a rare autosomal recessive lysosomal disorder that often proves fatal within the first year. A key diagnostic indicator is the presence of normally shaped, bilaterally enlarged adrenal glands with dense cortical calcifications, detectable via prenatal ultrasound, improving management.
Conflicts of Interest:
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sen D, Satija L, Saxena S, Rastogi V, Singh M. A rare constellation of imaging findings in Wolman disease. Med J Armed Forces India. dec 2015;71(Suppl 2):S448‑51.
- Sadhukhan M, Saha A, Vara R, Bhaduri B. Infant case of lysosomal acid lipase deficiency: Wolman’s disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2014 May 15;2014: bcr2013202652.